
Close

India has solidified its position as a global hub for multinational corporations (MNCs) seeking to establish Global Capability Centers (GCCs). These centers, often known as Global In-House Centers (GICs), have evolved from being cost-saving units to innovation-driven hubs that foster operational excellence. Currently hosting over 1,800 GCCs, India accounts for nearly 50% of the world’s GCC footprint. By 2030, the number of GCCs in India is expected to exceed 2,000, generating revenues of $99–$105 billion annually.
Here’s a comprehensive guide to turning your GCC setup in India into a reality, leveraging India’s unique advantages.
1. Cost Efficiency

India offers unparalleled cost advantages. Salaries for highly skilled professionals are 30–50% lower than in Western markets, while real estate costs are significantly more affordable, particularly in Tier-II and Tier-III cities like Kochi and Coimbatore. Survey insights reveal that companies establishing GCCs in India report up to a 70% reduction in IT talent acquisition costs and a 40% reduction in infrastructure expenses.
2. Access to Skilled Talent
India’s workforce is one of the largest and most qualified globally. Producing over 2.3 million STEM graduates annually, the country ensures a continuous supply of talent specializing in emerging fields like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and data science. This makes setting up a GCC in India an attractive prospect for companies prioritizing innovation and operational efficiency.
3. Government Incentives
Supportive policies amplify India’s appeal as a GCC destination. Relaxed foreign direct investment (FDI) norms, tax benefits in Special Economic Zones (SEZs), and state-specific GCC initiatives contribute to the growth of India’s GCC ecosystem. For example, Karnataka’s GCC policy (2024–2029) aims to establish 500 new GCCs by 2030, providing subsidies for capital expenditure, talent development, and operational costs.
4. Thriving Ecosystem
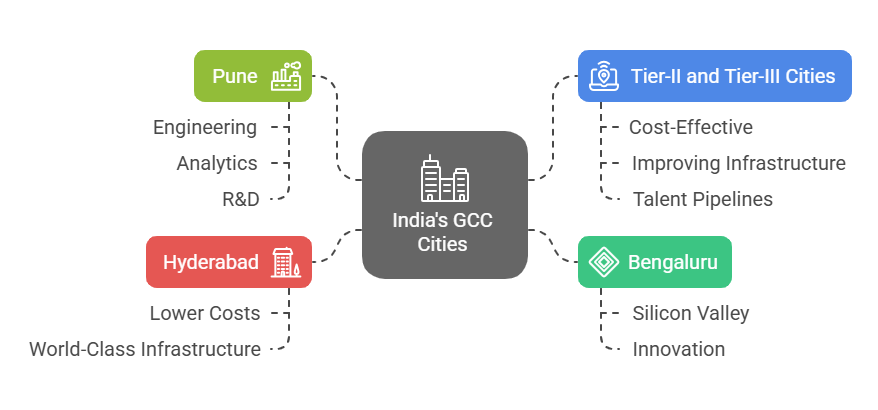
India’s robust digital infrastructure, vibrant startup culture, and regulatory support contribute to a thriving ecosystem. Cities like Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Pune are established GCC hubs, while Tier-II and Tier-III cities are emerging as cost-effective alternatives with growing infrastructure and talent availability.
India is home to a lot of major cities that are popular destinations for Global Capability Centers, and several cities have emerged as a prominent hub for MNCs. Each city has its own unique advantage and that each city caters to various sectors and business needs. Here’s an overview of the key GCC hubs in India.
1. Define Strategic Goals
Begin by aligning your GCC objectives with your company’s broader vision. Whether your focus is on cost optimization, innovation, or customer experience enhancement, this clarity will guide your feasibility studies, location selection, and operational planning.
2. Conduct a Feasibility Study
Evaluate the market potential, regulatory requirements, and cost structures. For instance, Bengaluru offers unparalleled access to experienced talent but comes at a higher operational cost. In contrast, cities like Ahmedabad or Jaipur provide more cost-effective alternatives without compromising on talent availability.
3. Choose the Right Location
Each of India’s top GCC cities offers unique advantages:
4. Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Ensure compliance with Indian corporate laws to streamline the setup process. This is an essential step in how to set up a GCC in India successfully. Key steps include preparing a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), Articles of Association, and obtaining Directors Identification Numbers (DIN). The largely digital process ensures faster execution.
5. Build a Skilled Team
Leverage India’s extensive talent pool by collaborating with local universities and training institutions to create tailored development programs. Companies like Microsoft and IBM have successfully partnered with premier institutions to cultivate specialized skills in AI, ML, and cybersecurity.
6. Operational Frameworks and SOPs
Establish clear Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) to define roles, responsibilities, and performance metrics. This ensures accountability and smooth day-to-day operations.
7. Leverage Technology
Incorporate cutting-edge technologies such as AI, generative AI, ML, and cloud computing to enhance operational efficiency and foster innovation. GCCs in India are increasingly using AI and RPA (Robotic Process Automation) to streamline processes and reduce manual workloads.
1. DIY Model
In this model, companies establish and operate GCCs independently, retaining full control and ownership. This approach suits organizations with robust internal resources and capabilities.
2. Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) Model
Here, a third-party provider sets up and initially manages the GCC. Once operational maturity is achieved, ownership is transferred to the parent company. The BOT model is particularly popular among companies new to India.
3. Hybrid Models
Combining elements of DIY and BOT, hybrid models allow for tailored approaches such as joint ventures or virtual captives, balancing control and operational flexibility.
1. High Attrition Rates
India’s competitive talent market often leads to high attrition in tech roles.
Solution: Foster an inclusive work culture with competitive benefits, clear career growth paths, and flexible work arrangements.
2. Regulatory Complexity
Navigating Indian laws, particularly in heavily regulated sectors, can be challenging.
Solution: Engage local legal and tax experts to ensure compliance and streamline operations.
3. Infrastructure Constraints
While Tier-II and Tier-III cities offer cost advantages, their infrastructure may not match that of metros.
Solution: Opt for SEZs or business parks designed for global operations.
Microsoft’s Global Capability Center (GCC) in Hyderabad exemplifies how companies can leverage India’s strengths. Initially focused on IT support, the center has evolved into a hub for AI and cloud innovation. With over 8,000 employees, it plays a critical role in Microsoft’s global strategy, driving innovation while significantly reducing operational costs.
India’s GCC ecosystem is poised for transformative growth. Key trends include:
Establishing a GCC in India is not just a cost-saving measure—it’s a strategic move to drive innovation, efficiency, and growth. By leveraging India’s cost advantages, skilled talent, and supportive ecosystem, businesses can transform their GCCs into centers of excellence. With meticulous planning and a clear vision, your GCC setup in India can become a cornerstone of your global strategy, delivering long-term value and competitive advantage.
We co-create with our customers at the center, combining deep domain expertise with innovative technology and talent solutions to accelerate growth. Our passion for excellence drives us to transform businesses, unlocking new opportunities and delivering lasting impact.
Subscribe to our newsletter to get our newest articles instantly!
Smart Leaders Are Rethinking Outsourcing. Are You? As global businesses face margin pressure and tech talent gaps, outsourcing is evolving from a cost play to a growth strategy. We're inviting senior leaders to share their perspectives in a short survey that explores how companies are scaling faster and operating leaner through smarter outsourcing. Take the short survey now and lead the next wave of global delivery excellence.
